Posted by David Fellows and John Leonardo[1]
Corruption is highly damaging to economic and social life through misappropriation of public funds, restriction of open market activity, favouritism towards families of those in power, and the many detrimental effects of rent seeking. In this piece we review evidence for the power of transparency to reduce corruption and improve economic performance. We then consider the increasing relevance of digital media, particularly social media, to the transparency agenda and how its application can be encouraged.
Economic performance, transparency and corruption
The IMF’s ‘Framework for Enhanced Fund Engagement’ 2018 noted that (i) transparency is significantly correlated with a perceptions-based indicator of the control of corruption; (ii) higher levels of corruption are typically correlated with lower growth; and (iii) corruption and governance are significantly associated with average long-run per capita growth, investment, and revenue. The IMF’s Fiscal Monitor: Curbing Corruption (April 2019 edition) shows that the least corrupt governments can collect considerably more in taxes than those at the same level of economic development. In a blog announcing this guidance Christine Lagarde, then Managing Director of the IMF, affirmed the importance of transparency by commenting that; ‘At the end of the day, the most durable “cure” for corruption is strong, transparent, and accountable institutions’.
How governments may involve digital media
The World Bank Document ‘Enhancing Government Effectiveness and Transparency: The Fight Against Corruption’ (September 2020) details studies in which developing countries have sought to combat corruption by improving transparency.
It instances:
- The identification of corruption relating to infrastructure projects in Columbia by the Government urging citizens to publicize unfinished projects.
- The introduction of participatory budgeting in Brazil where one study found that adopter municipalities achieved a 39% higher tax collection than those that had not.
- The use of Beneficial Ownership declarations in the Ukraine where online access to records promises significant advantages following a chequered introductory experience.
- Public reporting of Supreme Audit Institution (SIA) findings in Ghana, and India’s practice of encouraging the public to comment on SIA reports and provide evidence of misdeeds.
These are all public engagement activities that can most readily be undertaken via digital media.
The impact of social media
Social media is a growing phenomenon across the developing world. It can be used by governments to encourage citizens to make their views known (figures in million).
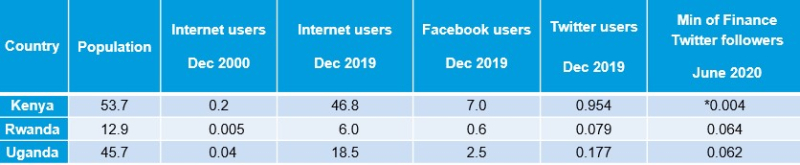
Note: *Kenya’s Anti-Corruption Agency has 293,000 Twitter followers
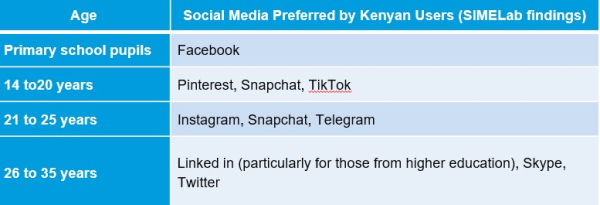
A survey of Kenyan social media users conducted by SIMELab in 2020 suggested that social media use was becoming highly age specific.
The survey identified the three most used media as WhatsApp (89%), Facebook (82%) and YouTube (58%). TIFA Research has identified Facebook as the current most effective advertising platform.
The African public accountability movement Connected Development (CODE) based in Nigeria uses digital media to help marginalised communities monitor public service investment employing its ‘follow the money’ slogan. A current focus is COVID-19 expenditure.
We have analysed the correlation between Transparency International’s 2019 CPI scores for the 48 best performing African Countries included in the index where both Facebook and Twitter services were available. There are strong positive correlations between social media user numbers and perceived corruption levels. This result seems consistent with the transparency/corruption relationship found in the IMF Framework for Enhanced Fund Engagement, reflecting public interest in government affairs and corruption.
A growing relationship between formal digital media and social media
Over the past year online news media have reported government initiatives against corruption and investigated acts of corruption. Two examples:
- On 11th November the Cyprus Mail commented that: ‘without (greater) public support, anti-corruption groups are unlikely to attain their objectives, because the politicians will have no reason to take any notice of them’.
- On 21stNovember 2020 ABS-CBN News reported that a task force investigating Philippine Government corruption led by Justice Secretary Menardo Guevarra had received at least 60 complaints during the previous two weeks.
These causes could benefit from social media use by community activists (Cyprus) and the government (Philippines).
Conclusions
The economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on developing countries brings the prospect of reduced national resources unless and until these countries can address their corruption challenges.
Formal online media have helped increase transparency in recent times. Further, social media is fast becoming an important form of popular communication throughout the developing world. The targeted use of social media platforms presents an effective opportunity for online public engagement that makes messaging easy to assimilate and respond to.
Governments can use social media to seek public support for reporting anti-corruption activities, complaining about unfair decisions and exposing the accumulation of unexplained wealth by politicians and officials. Such engagement is, however, dependent on the demonstration of government integrity, the recognition of public priorities, and the provision of basic information on services and funding to local communities.
The international development community can encourage governments to uphold press freedom, protect whistle-blowers and use social media as part of the transparency process, and scale up its support to countries that are pursuing effective anti-corruption policies.
[1] David Fellows is an international development PFM advisor who previously worked extensively in UK local government finance and in the Cabinet Office. He was a leader for the introduction of digital communication in UK public service delivery. John Leonardo is a PFM expert with extensive worldwide experience. They are both directors of PFMConnect, a public financial management consultancy (david.fellows@pfmconnect.com).
Note: The posts on the IMF PFM Blog should not be reported as representing the views of the IMF. The views expressed are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of the IMF or IMF policy.