Posted by Yasemin Hurcan[1]

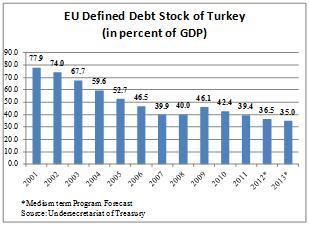
Inten years that followed the 2001 economic crisis in the country, Turkey managed to halve its debt to GDP ratio.As a result, Turkey was selected as a benchmark country for debt reduction in theWorld Bank’s 2012 report “Golden Growth: Restoring the Lustre of the EuropeanEconomic Model”. A recently published book[2] entitled “Treasury Operations in Turkey andContemporary Sovereign Treasury Management” discusses how the Turkish Treasury managed to decreaseits debt by, amongst other things, restructuring the Treasury’s operations andmanagement. The publication is available as an e-book.
 Eachsection of the book was written by one or more members of staff of the Turkish Treasurywho actively took part in the reforms of the early 2000s, when Treasuryoperations in Turkey went through radical changes. The book looks at the Treasury’soperations and management as part of an integrated balance sheet. As such, itcovers not only cash and debt management but also guarantees issued by theTreasury, public-private partnership projects, non-guaranteed publicliabilities and other contingent liabilities, financial receivables, and riskmanagement.
Eachsection of the book was written by one or more members of staff of the Turkish Treasurywho actively took part in the reforms of the early 2000s, when Treasuryoperations in Turkey went through radical changes. The book looks at the Treasury’soperations and management as part of an integrated balance sheet. As such, itcovers not only cash and debt management but also guarantees issued by theTreasury, public-private partnership projects, non-guaranteed publicliabilities and other contingent liabilities, financial receivables, and riskmanagement.
Afterdiscussing the weaknesses in Treasury operations and management which contributedto the 2001 crisis, each chapter of the book elaborates on how the scope of Treasurymanagement has changed in the decade since. While its focus is on the history ofthe transformation of the legal and operational structures of the TurkishTreasury, it also addresses contemporary ideas and practices of treasurymanagement through the experience of Turkey.
Thefirst three chapters discuss public debt management, its transformation and interactionwith macroeconomic policies, and debt management policies. These chaptersexplain how the Turkish Treasury changed the legal and institutional frameworkof public debt management to, amongst other things, improve the coordination withmonetary and fiscal policies.Thefollowing five chapters cover risk management practices at the Treasury,including an evaluation of: (i) the methods used to assess debt sustainabilityand undertake sensitivity analyses; (ii) systemic risks from a debt managementviewpoint; (iii) the management of assets and liabilities; (iv) benchmarkborrowing strategies and the main outcomes of these strategies; and (v) credit risk management. Chapters9, 10, 11, and 12 look at: (i) the general framework of domestic and externaldebt from an historical perspective and the development of domestic debtmarkets; (ii) cash management practices, as second-tier Treasury operations, andthe process of moving from cashrationing to active cash management; and (iii) management of treasuryreceivables through monitoring and sanctions. The final two chapters discussthe operational risk and accounting practices in Treasury operations.It is to be hoped that the book will be useful both tostudents of political and financial developments in Turkey, but also topractitioners in other middle-income countries who are contemplating reform oftheir national treasuries.
Note: The posts on the IMF PFM Blog should not be reported as representing the views of the IMF. The views expressed are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of the IMF or IMF policy.